2D Topology, Revision, and Defeaturing
What is Topology
Topology is how surfaces are connected to adjacent surfaces of a part.
- Surface connectivity is controlled by the associated surface edges
- If a surface edge is associated with more than 1 surface, those surfaces are considered to be connected (“equivalenced”)
- Surface edges are categorized, named, and colored according to the number of associated surfaces
To learn more about topology, revision and defeaturing, select one of the topics below.
Connectivity is really important, and critical at the same time, when you need to create a contiguous mesh over connected faces thus guaranteeing stresses, strains and deformations that will propagate over the part in a realistic manner. HyperMesh uses a tolerance calculation to determine when two or more edges should be connected and provide tools to fix connectivity issues before meshing.
HyperMesh allows easy visualization of surface connectivity through the use of an edge color scheme shown below:
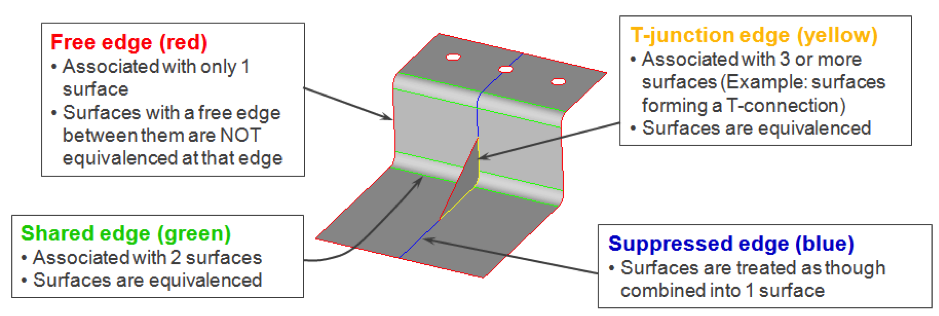
Topology Visualization
In the HyperMesh Visualization toolbar, the Topology Options Icon ![]() will open the Visualization tab > Topology icon
will open the Visualization tab > Topology icon ![]() .
.
This tab will allow the user to:
- display or hide 2D and 3D topology based on its type
- control the transparency
- change the shading colors of mappable solid regions.
Topology display mode (By Topo) is a default for some panels (Surface Edit, Quick Edit, Point Edit, Edge Edit, Autocleanup, and Automesh).
Display of the topology can be controlled with the Geometry Color Mode icon ![]() included in the HyperMesh Visualization toolbar.
included in the HyperMesh Visualization toolbar.
Topology Repair: General Process
HyperMesh will in most cases create proper and connected geometry accurately representing the initial CAD geometry.
In some cases you need to work with topology to repair geometry.
The general process is the following:
- Figure out what the ideal surface connectivity of the part should be.
- Observe the current display of topology colors (free, shared, t-junction). Figure out what is causing the topology to be displayed this way.
- Use the tools in HyperMesh that get the connectivity from what it is to what it should be as quickly and efficiently as possible.
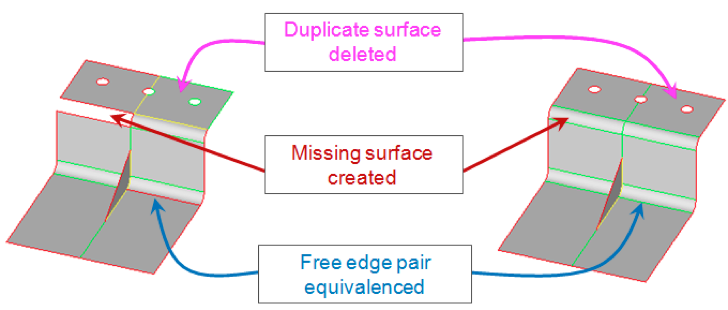
Topology Repair: Tools
HyperMesh has a supply of tools to repair issues in the geometry.
Below you can find the tools that HyperMesh provides:
- Quick Edit panel (Geometry > Quick Edit or F11)
The Quick Edit panel is a “tool box” of utilities for geometry repair. Many of the tools can be found in other panels and their functionality is exactly the same. The Quick Edit panel simply provides a single location for many of the most often used tools. Mouse over each tool for a description.
Edge Edit panel (Geometry > Edit > Surface Edges)

- toggle-(2 edges pair at a time) toggles edges from one state to another (free > shared > suppressed, by clicking with the left mouse button) based on the cleanup tolerance setting.
- (un)suppress-Selects multiple edges to suppress, all of them at once
- replace-(1 edge pair at a time) combines two edges into a shared edge at the location of one of the original edges, controlling which edge to retain and which to move.
- equivalence-(multiple edges at a time) searches for free edges and combine them with a matching edge within the cleanup tolerance.
- unsplit-removes previously created split-lines
- edge fillets-removes fillets from surface edges.
- by feature-combines surfaces based on geometric features (angle surfs and offset surfs )
Point Edit panel (Geometry > Edit > Fixed Points)
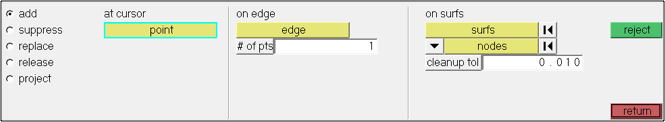
- add-Adds new points to the model geometry to help control mesh pattern (especially helpful along edges to control node seeding)
- suppress-"Turn off" points in the model geometry. The points are not deleted; they are ignored when meshing.
- replace-Combines 2 fixed points together at a single location; moves one point to another, combining them into a single point.
- release- Use this panel to "release" vertices so that they become free (unattached points) and any shared (green) edges that they were attached to the point become free (red) edges.
- project-Projects fixed points onto a nearby edge (Useful for aligning mesh between 2 edges).
Surface panel (Geometry > Create > Surfaces > Spline/Filler)

- Spline/Filler (
 ): Creates surfaces by filling in gaps, such as a hole in an existing surface.
): Creates surfaces by filling in gaps, such as a hole in an existing surface.
- The Keep tangency option is valid for surface edge line selection only. It considers curvature of any surfaces attached to the selected edges and tries to create a surface tangent to them. This helps to form a smooth transition to the surrounding surfaces.
- The Auto create (free edges only) option is valid for free surface edge line selection only. It simplifies the selection of the lines bounding the missing surface. Once a line is selected, HyperMesh automatically selects the remaining free edges that form a closed loop, and then create the filler surface.
This section looks at changing the shape of a part in order to simplify the geometry. Certain details of the shape, such as small holes or blends, may simply not be necessary for the analysis being performed. When these details are removed, the analysis can run more efficiently. Additionally, mesh quality is often improved as well. Changing the geometry to match the desired shape can also allow a mesh to be created more quickly.
Defeaturing
There are many features on a part that are not critical to the structure of the part and have little or no effect on the analysis. These features can include
- Lightening Holes – For part weight reduction
- Edge Filets – For reduction of sharp corners allowing safer part handling
- Surface Fillets – To meet manufacturing requirements
These features often are process driven and are not function critical. While our goal is to mesh a part that as closely as possible accurately represents the geometry, these features often degrade the quality of the mesh. As such they can be defeatured out of the design allowing for a substantially improved mesh with little impact on the results.
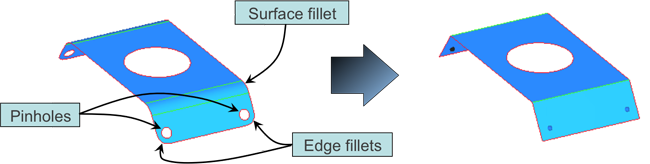
Defeaturing Tools
The defeature panel, opened by selecting Geometry > Defeature, allows you to find and delete pinholes, fillets on surfaces and surface edges, and duplicate surfaces. Each of the sub-panels allows you to manually select the feature that you wish to delete, but also supports a three-step process that can locate such features for you. Click the subpanels below to see a short description.