axis
Sets the scaling and range of x, y, and z axes (x by default). Called without arguments, axis turns autoscaling on.
Syntax
axis()
axis([X_lo X_hi])
axis([X_lo X_hi Y_lo Y_hi])
axis([X_lo X_hi Y_lo Y_hi Z_lo Z_hi])
axis(option)
Inputs
- X_lo, X_hi
- Lowest and highest x ranges.
- Y_lo, Y_hi
- Lowest and highest y ranges.
- Z_lo, Z_hi
- Lowest and highest z ranges.
- option
- Takes one of the following values:
- 'equal'
- Sets uniform aspect ratio to the axes (2D plots only).
- 'normal'
- Resets the aspect ratio (2D plots only).
- 'on'
- Enables the visibility of the axes' tics and labels.
- 'off'
- Disables the visibility of the axes' tics and labels.
- 'square'
- Sets square aspect ratio to the axes (2D plots only).
Examples
clf;
x=linspace(-pi,pi, 100);
plot(x,sin(x));
axis ([-4 4 -1.5 1.5])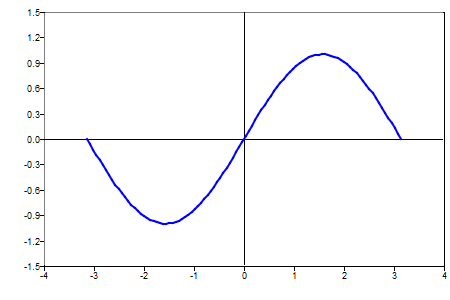
Figure 1. Simple axis example
clf;
x=linspace(-pi,pi, 100);
plot(x,sin(x));
axis('equal');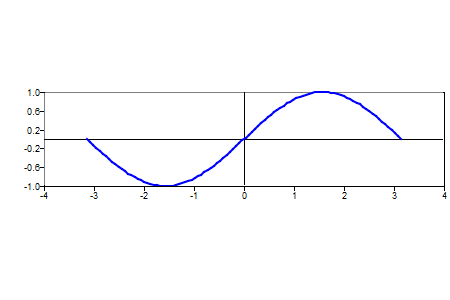
Figure 2. Uniform aspect ratio
clf;
x=linspace(-pi,pi, 100);
plot(x,sin(x));
axis('square');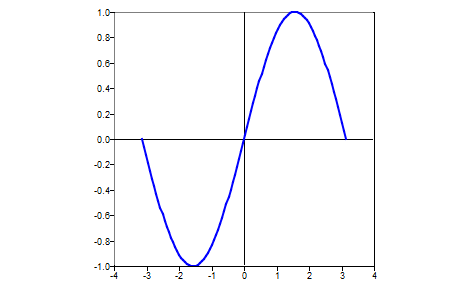
Figure 3. Square aspect ratio