The native CAD model is imported using CAD readers in HyperMesh that are run in the background, and exported in different
HyperMesh versions over two sessions. Exported models are
superposed and compared using advanced CAD-CAD comparison, and any loss of geometric data is
identified along with any entity changes. A reference report is also created.
-
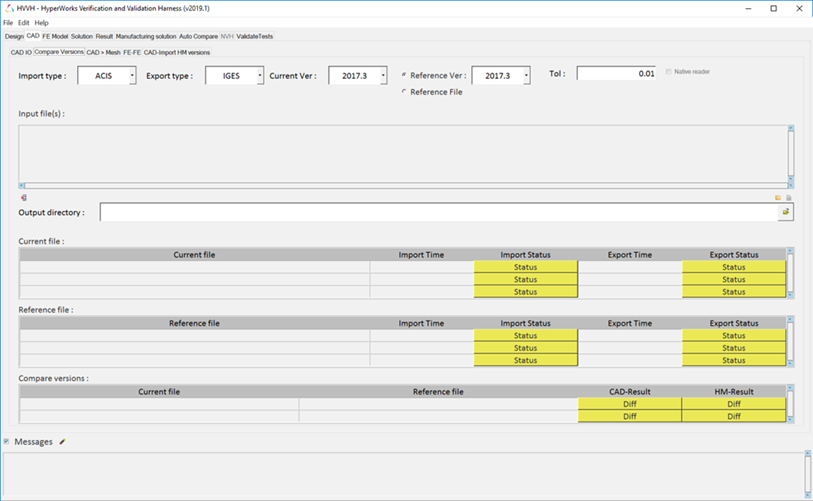
Click the CAD tab then the Compare
Versions tab.
-
Select a CAD input file from the first drop-down menu.
Supported file types include:
-
Select an output file type from the second drop-down menu.
Supported file types include:
-
Specify a current and reference HyperMesh version
number.
-
Enter a Tolerance value for use in the comparison.
Tip: Click
Native Reader to enable a native
reader. Original CAD software and licenses must be used. Only available for
the UG format.
This method of import, along with feature-based meshing
technology, provides a robust way to create high-quality CAE solid
tetrahedral mesh models without a lot of geometry cleanup.
-
Input files.
-
If you select Reference File instead
of Reference Version, the GUI changes slightly. Select
Reference File to compare your file with a reference
file or previously certified file.
-
Select an output directory.
-
Click Import/Export to input your source file and output
your result information.
The time and status at import and export for each file is displayed in
the Current and Reference file tables. Click Diff in the
Compare versions table to view the report which lists the difference between the
reference file (the input deck) and the HyperMesh
exported file.
Tip:
- The message log file displays
the current status of processes in progress. Click
Status/Diff to display the respective
report. The message log file is a text file and is saved to your
output directory.
- Click Html
Report to generate an HTML report of your
session information for any number of files run through the
process.