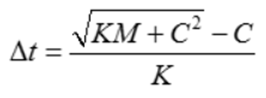Radioss Interface
Overview of the Radioss interface.
HyperMesh provides a complete pre-processing environment for preparing Radioss data decks for analysis.
HyperMesh can read existing Radioss decks, create a model, display and edit Radioss cards as they will look in the deck, and write a deck for analysis.
To create Radioss decks in HyperMesh, you must load the Radioss user profile with the appropriate template to access the full pre-processing capability.
Import and Export
- HyperMesh supports Radioss solver versions for import and export till Radioss 2020.
- Solver specific import options are available in the Solver Options tab.
- HyperMesh supports Radioss Dummy models.
- Most IDs in the solver deck are preserved in HyperMesh. If a keyword is not supported in a dedicated HyperMesh entity to ensure its unique ID-Pool, then HyperMesh renumbers those keywords when ID conflicts are detected. The new IDs are posted during the import process.
- The Radioss interface supports a smart, reliable FE input reader that warns you when your input deck contains unsupported fields and unsupported data lines.
- HyperMesh supports undefined entities. These are entity IDs which are referenced in keywords (for example a Material ID in a *PART) but not defined in the deck. In this case, HyperMesh creates a default card (for example a material of type elastic is then created) in order to preserve the ID. This keyword has the Defined checkbox toggled off and is automatically not exported.
Duplicate ID’s
- Several Radioss keywords are mapped to one HyperMesh entity in some instances. By default, the Radioss interface does not allow duplicate IDs within the same HyperMesh entity, with the exception of elements. Radioss does allow duplicate IDs across cards mapped to one HyperMesh entity. In HyperMesh, ID flexibility similar to Radioss can be enabled by selecting and activating the allow duplicate IDs option.
- Duplicate IDs are supported for the following HyperMesh entities in the Radioss user profile: elements, properties, entity sets, and sensors.
Rigid Body Management
Any RBODY created with less than 10000 slave nodes is shown with the spider connecting the master node to the slave nodes. If the RBODY has more than 10000 slave nodes, then it is shown with a single link connecting the master node to one of the slave node. All other options are similar for both.
Mass Calculation
Elemental Time Step Calculations
Time Step Calculations
Critical Time Step for Shell (2D) Elements
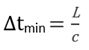
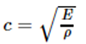
Where E is Young's modulus and ρ is Material density.
Critical Time Step for Solid (3D) Elements
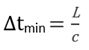
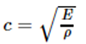
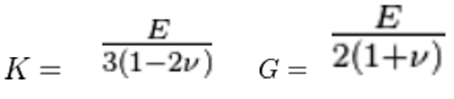
Where, E is Young’s modulus, ρ is Material density, 𝜐 is Poisson’s ratio, K is Bulk Modulus, G is Shear Modulus.
Critical Time Step for Beam (1D) Elements
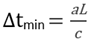
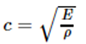
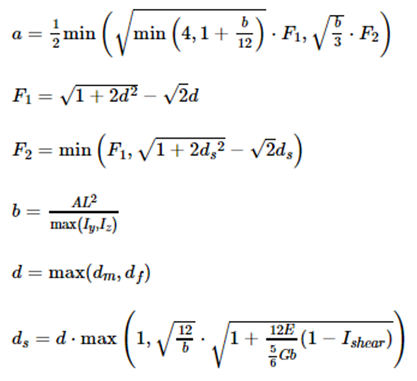
Critical Time Step for Spring/Discrete Elements