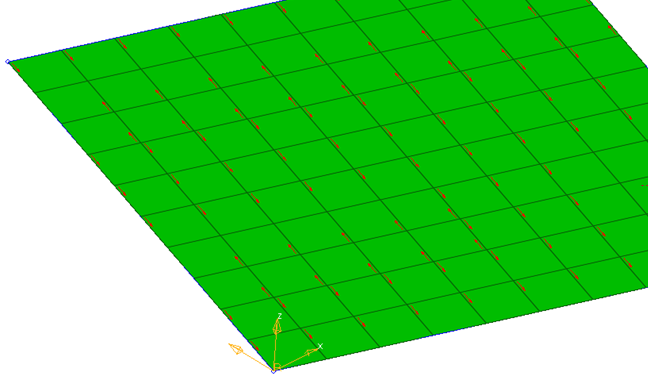
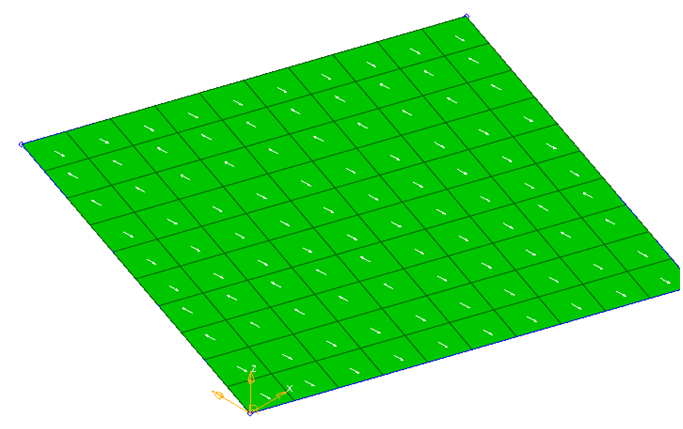
Material Orientation
The Material Orientation tool provides several methods of assigning material x directions for shell and solid elements, and additionally z directions for solid elements.
- Select the Entities on which to assign material orientation, either Elements or Properties.
- Set the Color of orientation vectors drawn after applying material orientation.
- To set the scale of orientation vectors drawn after applying material orientation, set Scaling Option to Auto or Manual.
- Type a value into the Size field for the manual input for size of orientation vectors drawn after applying material orientation.
- Set the X direction method. Choose from the following:
- Curve – spatially map input curve(s) as the x direction
- Lines/Edges – lines which define the orientation
- Flip direction – for lines/edges only. Determines whether the curve provided is +x direction or -x direction.
- Nodes – list of lines that define the orientation
- System ID – system assigned as orientation
- System Axis – system and axis of system to map as x direction
- Angle – for OptiStruct and Nastran only. Directly enter rotation applied on THETA field of element.
- Curve – spatially map input curve(s) as the x direction
- Set a value for Normal by choosing one of the
following:
- Element Normal – uses element z direction (can be viewed from panel if elements are selected). Typically, this option should be used.
- Surface Normal – aligns material z direction spatially to selected surface.
By Curve
- Select the elements for which a new material angle will be assigned.
- Select the lines or list of nodes to define the material direction. The
element centroid will be taken and projected to the closest line/node
segments and the line tangent direction will be found to assign the material
angle.Figure 1. A Circular Pattern of the Material Orientation is Assigned Based on the Outer Circular Line Direction
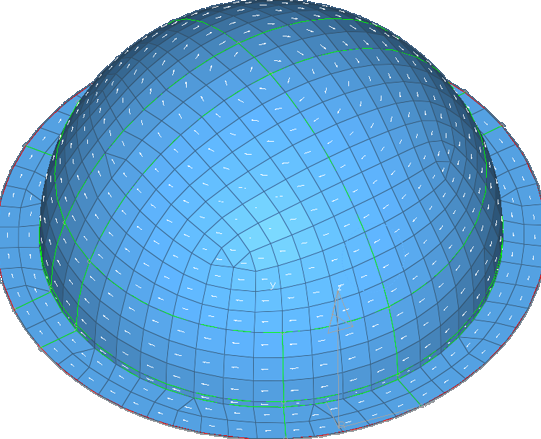
Other material orientation tools are also available.
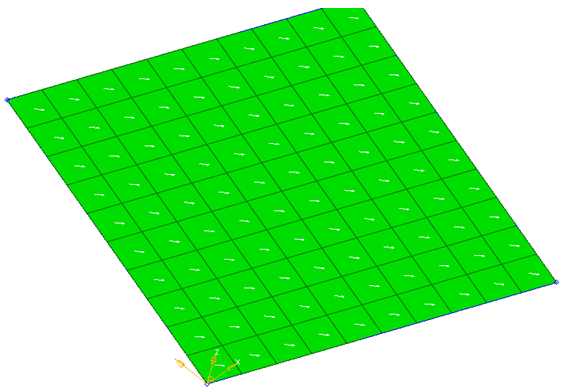
By System ID
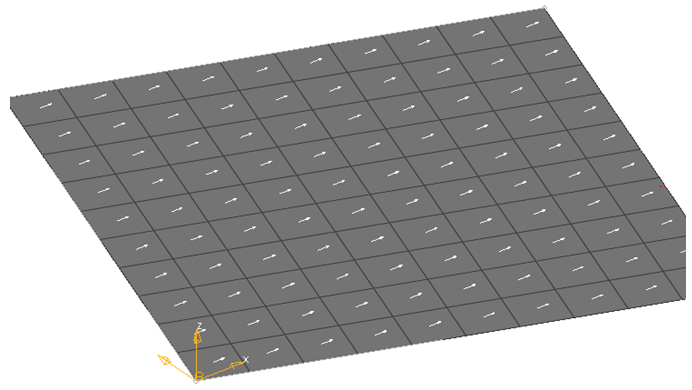
By System Axis
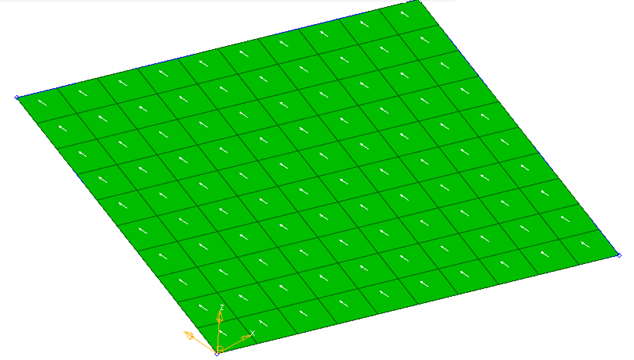
By Angle