Fluid-Structure Interaction
OptiStruct and AcuSolve are fully-integrated to perform a Direct Coupled Fluid-Structure Interaction (DC-FSI) Analysis based on a partitioned staggered approach.
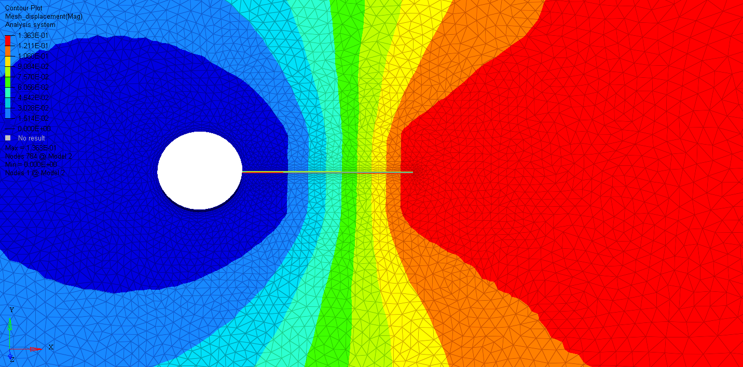
Figure 1. Fluid-Structure Interaction between a Solid Plate and Enclosing Fluid
As the name suggests, Fluid-Structure Interaction simulates the interrelationship between fluid flow and the solid body the fluid is in contact with. The behavior of the structure affects the fluid and vice-versa in a coupled dynamic interaction that is captured by dividing the time domain into time steps. For each time step, the exchanged solution attributes are solved for from the governing equations until equilibrium convergence is attained. Each such iteration run through towards convergence within a time step is known as an exchange (in OptiStruct) or a stagger (in AcuSolve). The fluid flow can be external to the solid object, similar to an aircraft wing moving through air, or it can be internal, like the flow of coolant in a condenser tube.
Target Applications
Supported Solutions
- Structural Fluid-Structure Interaction (Nonlinear Direct Transient Structural Response of the structure).
- Thermal Fluid-Structure Interaction (Linear Transient Heat Transfer Response of the structure).
Combined structural and thermal heat transfer solutions in conjunction with fluid-structure interaction is currently not supported. You can either run Structural FSI or Thermal FSI, however, you cannot run both in the same run. In the following sections, SFSI refers to Structural Fluid-Structure Interaction and TFSI refers to Thermal Fluid-Structure Interaction for brevity and to avoid redundancy.