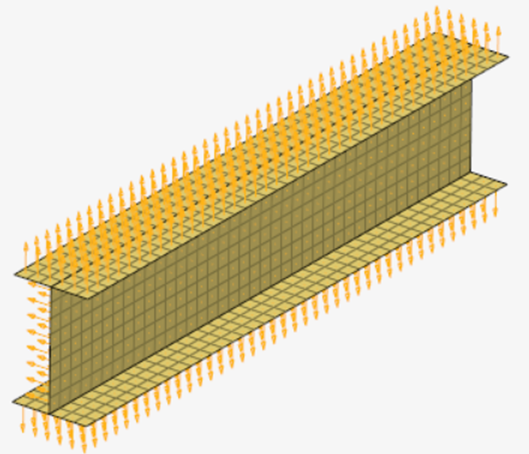
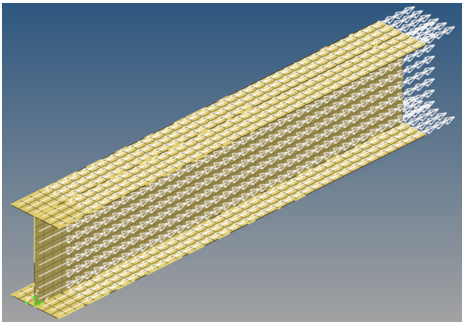
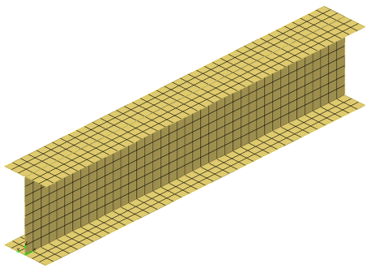
I-Beam Analysis
Step through the model build process for a composite I-beam model.
- Ply creation
- Set ply normals
- Sublaminate creation
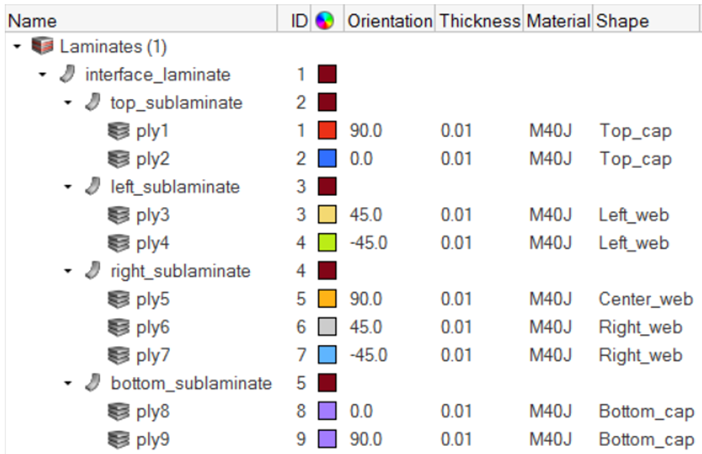
- Interface laminate creation
- Template property creation
- Surface geometry and mesh of I-beam
- Orthotropic material
- System collector that contains system used to assign material direction
- Unit system is PSI
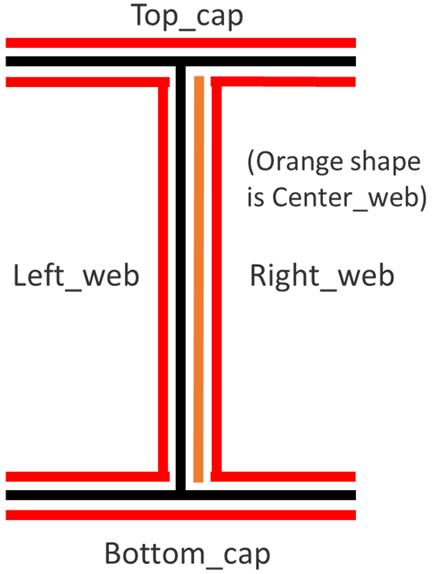
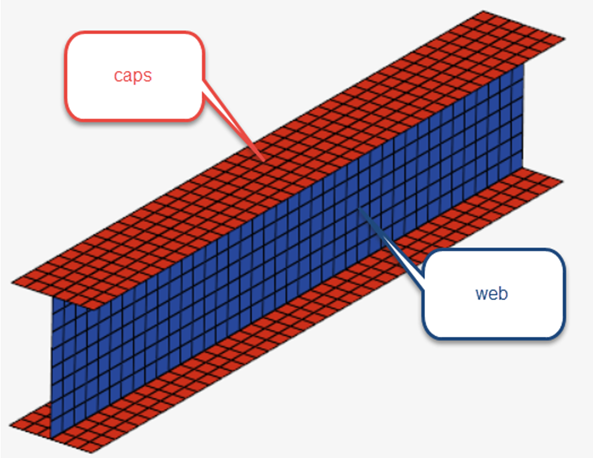
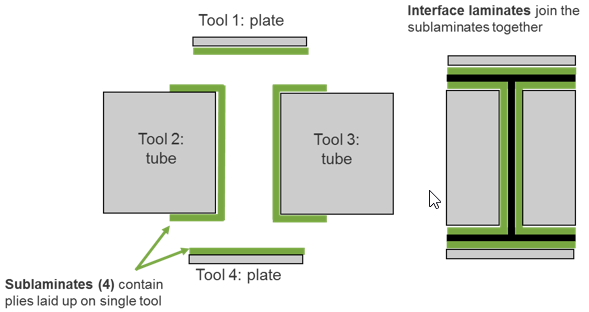
- The manufacturing process uses complex tooling to manufacture 4 sublaminates
(co-cured to form the final part):
- top cap on Tool 1
- bottom cap on Tool 4
- left web on Tool 2
- right web on Tool 3
Introduction
- Open HyperWorks.
- In the Solver Interface dialog, set the profile to OptiStruct.
- Open the model file, composite_beam.hm.
- Open the Composite Browser by clicking the Composite tool in the Model ribbon or .
Review Stacking Direction and Element Normals
Review stacking direction and element normals.
Review Material Reference Orientation
Review the assigned material reference orientation.
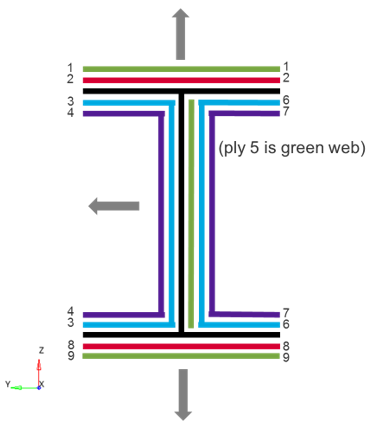
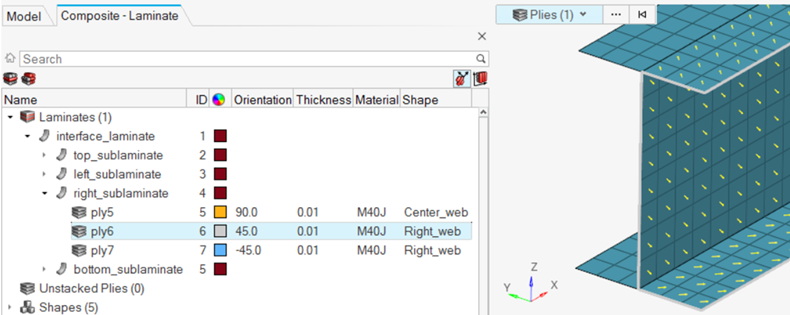
Create Plies
Create the plies that make up the composite laminate.
Set Ply Normals
Correct ply normals.
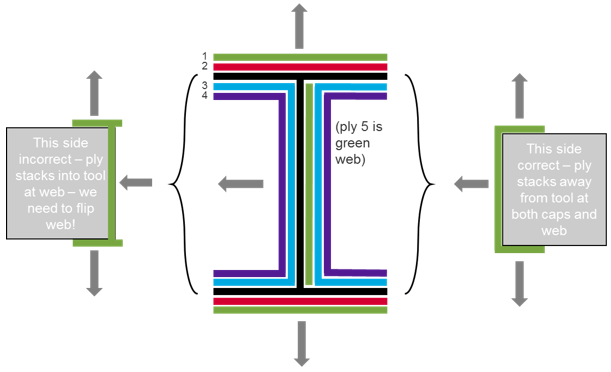
- From the Composite Browser white space context menu, click .
- Toggle the Select ply arrows so that ply3 is active.
- Click Apply to plot current ply normals. Note the discontinuity described above.
- To correct ply normals, click the twice to access the element selection panel.
- Select only elements of the web and click proceed.
- Click the Reverse radio button under Normals and then click Apply. This will plot corrected ply normals for ply3.
- Reset the Display radio button under Normals to prevent any additional changes.
- Confirm the web of ply3 has no discontinuity with the caps by repeating Step 2 and Step 3.
- Repeat Step 3 through Step 8 for ply4.
Create Sublaminates
Create the sublaminates, which represent the stacks up plies on each unique tool used to manufacture the part.
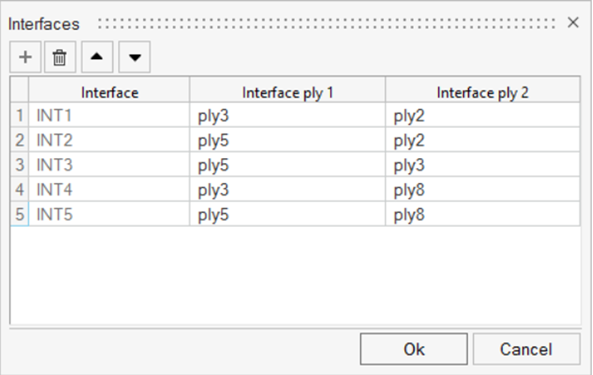
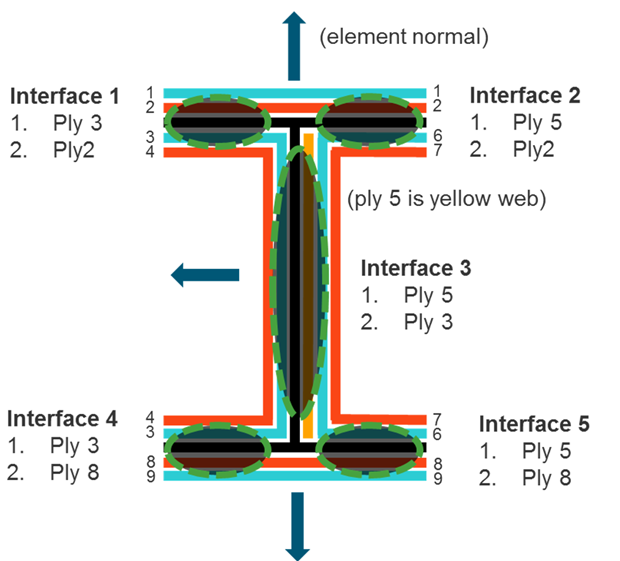
Create the Interface
Define the interface, which specifies how the sublaminates are joined.
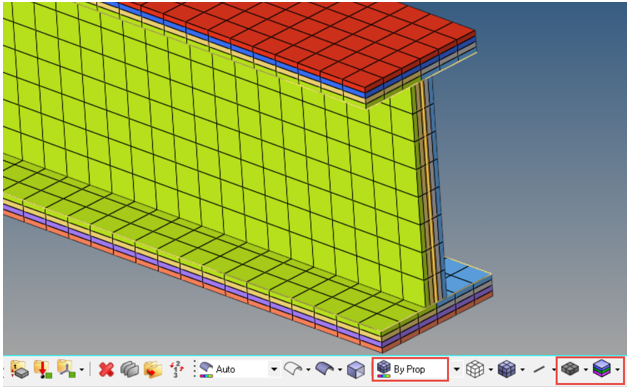
Create Ply-Based Properties
Create ply-based template properties.
Typically, only one ply-based property is required per part. However, for cases where portions of a part require different property attributes (offset is most common), multiple properties are required. For the I-beam model, the elements that make up the web are at the midplane of the laminate, and the elements that make up the caps are at the tube tooling surfaces.
Optional: Ply Direction Visualization
Plot vectors that represent the ply1 direction on each element.
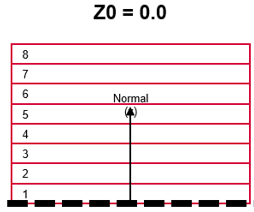
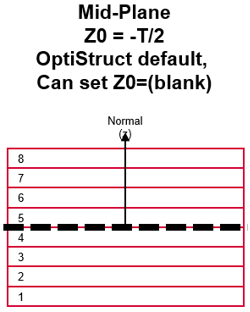
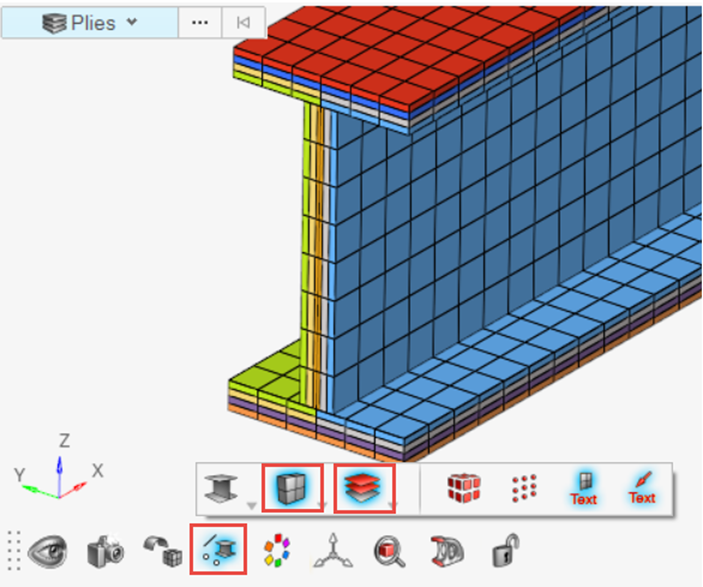
Optional: Composite Layers Visualization
Visualize the thickness and ply layers of the laminate. This is used to confirm that all plies are in the expected order. If the interfaces were defined incorrectly, there will be discontinuities where portions of a ply jump to an unexpected location in the full stack.