BatchMesher Midmesh Generation Rules
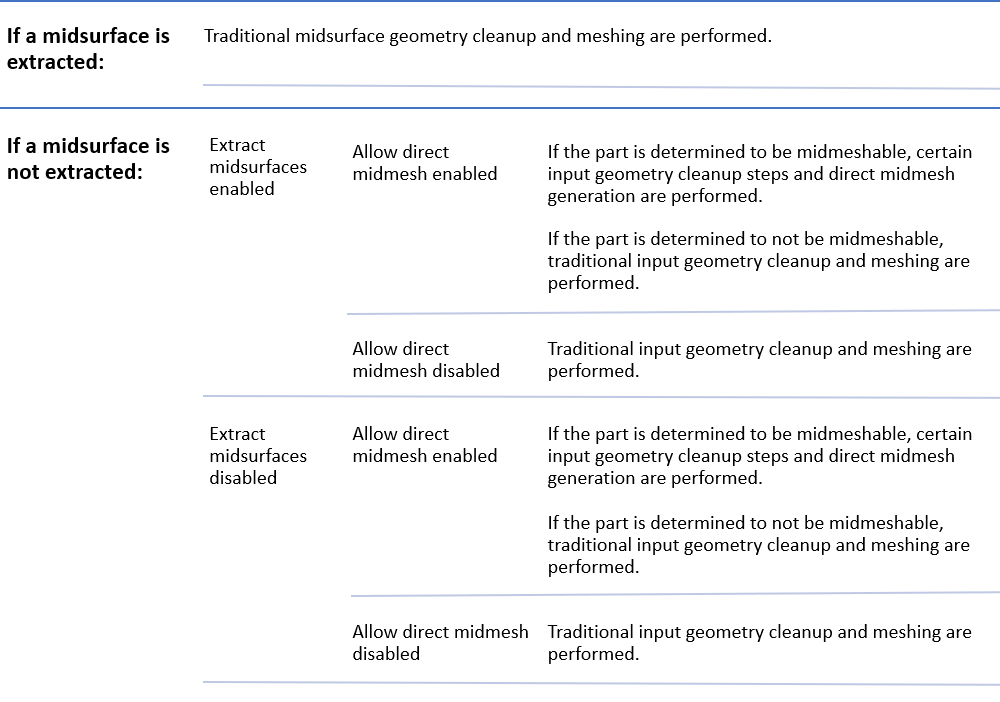
Midmesh generation is also supported from within BatchMesher.
View new features for HyperWorks 2020.
Learn the basics and discover the workspace.
Discover HyperWorks functionality with interactive tutorials.
Learn how to create, open, import and save models.
Solver interfaces supported in HyperWorks.
A solver interface is made up of a template and a FE-input reader.
Perform automatic checks on CAD models, and identify potential issues with geometry that may slow down the meshing process using the Verification and Comparison tools.
Create, organize, and manage the CAE parts.
Create, edit, and cleanup geometry.
Learn about the different types of mesh you can create in HyperWorks.
Edit the Parameter and Criteria files and define mesh controls using the Mesh Controls Browser.
1D mesh that allows accurate testing of connectors, such as bolts, and similar rod-like or bar-like objects that can be modeled as a simple line for FEA purposes.
A surface mesh or "shell mesh" represents model parts that are relatively two-dimensional, such as sheet metal or a hollow plastic cowl or case.
Use the General 2D Mesh tool to create 2D meshing with various algorithms.
Use the BatchMesher tool to perform geometry feature recognition, cleanup and automatic meshing in batch mode for given CAD files.
Use the CFD 2D Mesh tool to generate hybrid grids containing hexa/penta/tetra elements in the boundary layer and tetra elements in the core or fare field.
Use the Panel Mesh tool to generate and edit mapped panel mesh.
Use the Rigid Body Mesh tool to create a quick mesh to represent the topology of a rigid object.
Automatically generate a mesh at the midplane location, directly from the input geometry (components, elements, solids or surfaces), without first creating a midsurface.
Use the Midmesh: Automatic tool to automatically generate a mesh at the midplane location, directly from the input geometry (components, elements, solids or surfaces), without first creating a midsurface. This saves significant time over the traditional midsurface-based approach.
Use the Midmesh: Repair/Fill tool to repair midmesh by attempting to fix topological problems (holes/gaps/cracks, intersections, slivers, overlaps) in the mesh and remesh the face, or create a mesh within a closed topology loop, attempting to keep tangency.
Use the Midmesh: Create Midedge tool to create a midedge.
Use the Midmesh: Edit Topology tool to edit midmesh topology.
Use the Midmesh: Align tool to align the midmesh.
Midmesh generation is also supported from within BatchMesher.
Use the Feature Edges tool to create and edit mesh controls on an edge.
The Rebuild tool streamlines the process of remeshing existing meshes to generate a new mesh with good quality and flow. The rebuild mesh functionality utilizes the same parameter and criteria files used by BatchMesher to define the quality criteria and relevant mesh parameters. This algorithm saves significant time over the traditional automesh and quality correction approach.
Adaptive wrap meshing is a useful utility to get a clean, water tight shell mesh out of 2D mesh containing several intersecting parts and small gaps which do not need to be modeled.
EM Lattice meshing is a method to create an axis-parallel mesh for 2D and 1D geometry input.
Shrink wrap meshing is a method to create a simplified mesh of a complex model when high-precision models are not necessary, as is the case for powertrain components during crash analysis.
Create facets out of a scanned data set or node cloud data.
Volume mesh or "solid meshing" uses three-dimensional elements to represent fully 3D objects, such as solid parts or sheets of material that have enough thickness and surface variety that solid meshing makes more sense than 2D shell meshing.
Rapidly change the shape of the FE mesh without severely sacrificing the mesh quality and create, edit, and apply shapes for subsequent design optimization studies.
Create and edit 0D/1D entities and edit 2D elements.
Tools used for crash and safety analysis.
Multi-disciplinary design exploration and optimization tools.
Many essential utility tools using HyperWorks-Tcl have been developed over the years to support Aerospace customers. A few tools have been collected and upgraded to be compatible with this release.
Panels contains pre-processing and post-processing tools.
A surface mesh or "shell mesh" represents model parts that are relatively two-dimensional, such as sheet metal or a hollow plastic cowl or case.
Learn about the different types of mesh you can create in HyperWorks.
Automatically generate a mesh at the midplane location, directly from the input geometry (components, elements, solids or surfaces), without first creating a midsurface.
Midmesh generation is also supported from within BatchMesher.
ON THIS PAGE
Midmesh generation is also supported from within BatchMesher.

ON THIS PAGE
(c) 2020. Altair Engineering Inc. All Rights Reserved.