RD-E: 5200 Creep and Stress Relaxation
The purpose of this example is to introduce how to use typical visco-elastic material to simulate creep and stress relaxation tests.
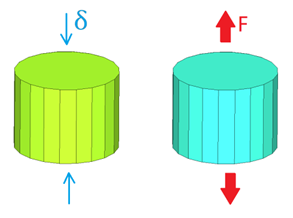
Figure 1.
Options and Keywords Used
- /MAT/LAW40 (KELVINMAX)
- Boundary condition (/BCS)
- Rigid body (/RBODY)
- Concentrated force load (/CLOAD)
- Imposed displacement (/IMPDISP)
Input Files
- Creep and Stress Relaxation
- <install_directory>/hwsolvers/demos/radioss/example/52_creep_and_stress_relaxation/*
Model Description
- For stress relaxation test: The foam sample has been compressed until a given strain and kept in this state.
- For creep test: The foam sample has been tensile under constant force.

Figure 2. Problem Description
Units: mm, s, Mg, N, MPa
- Material Properties
- Initial density
- 2e-9 [Mg/mm3]
- Bulk modulus
- 66.67
- Long time shear modulus Ginf
- 10
- Shear modulus G1
- 90
- Decay constant
- 1 = 0.01 [1/ms]
Model Method
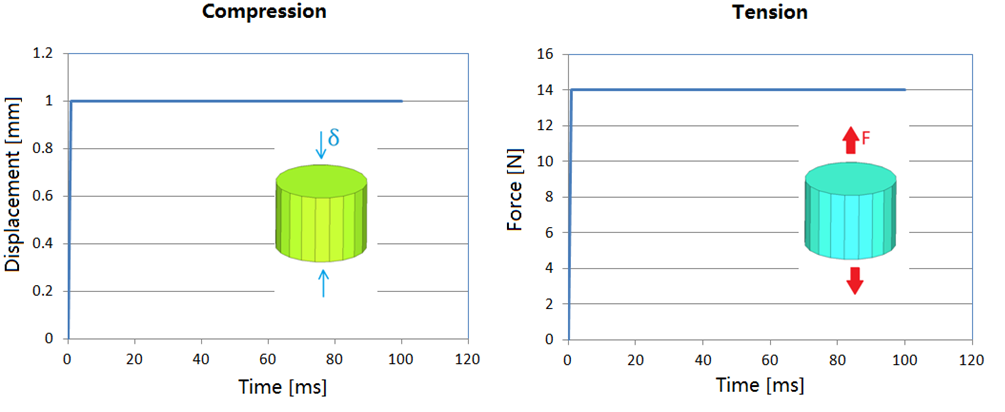
Figure 3. Stress Relaxation Test under Constant Displacement and Creep Test under Constant Force
For stress relaxation test: The foam sample has been compressed under constant displacement (/IMPDISP).
For creep test: The foam sample has been tensile under constant force (/CLOAD).
Results
Figure 4.
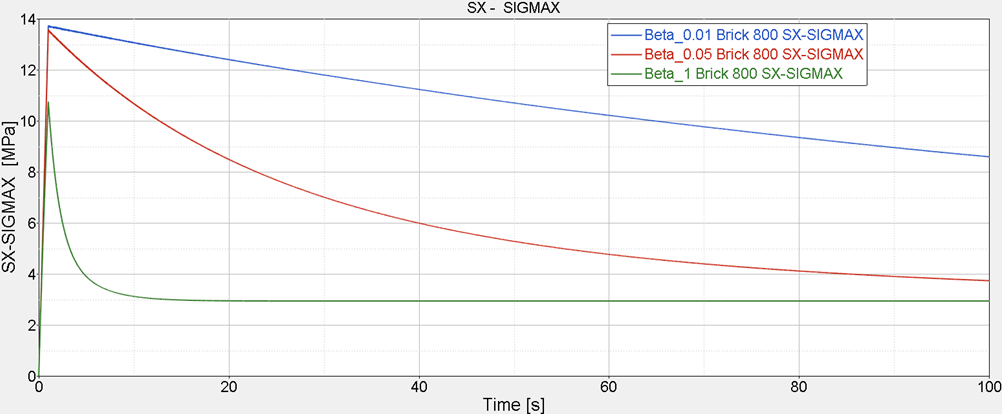
Figure 5. Stress Relieved with Different Decay Constant in Stress Relaxation Test under Constant Displacement
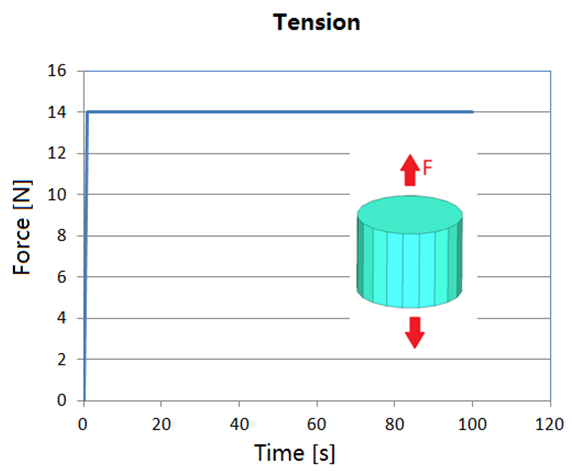
Figure 6.
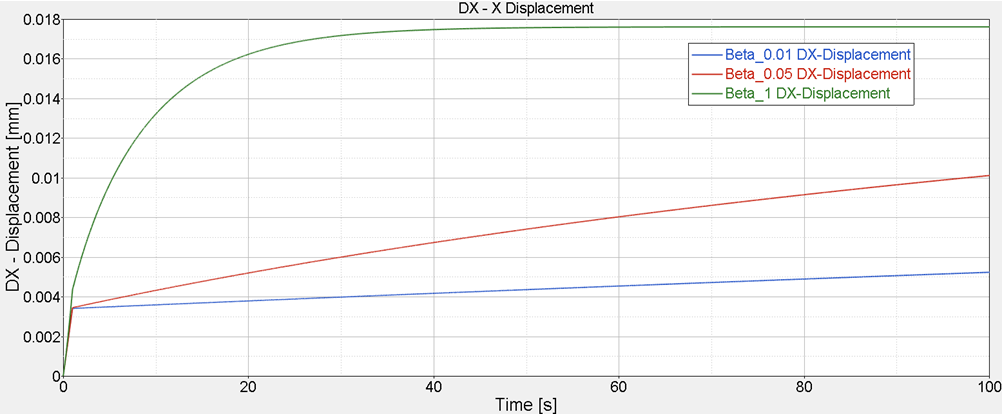
Figure 7. Sample Deformed with Decay Constant in Creep Test under Constant Force

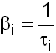 with
with 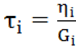
The general case of viscous materials represents time-dependent in elastic behavior. Creep is time-depended deformation and stress relaxation is a time-depended decrease in stress. Viscous material can describe these two phenomenons. In Radioss, the following material laws describe viscous:
Visco-elastic Law
- /MAT/LAW34
- Visco-elastic generalized Maxwell model, Boltzmann (solids)
- /MAT/LAW35
- Visco-elastic generalized Maxwell-Kelvin-Voigt (shells + solids)
- /MAT/LAW38
- Visco-elastic tabulated (solids)
- /MAT/LAW40
- Visco-elastic generalized Maxwell-Kelvin (solids)
- /MAT/LAW42
- Ogden/Mooney-Rivlin with Prony viscosity (Hyperelastic materials)
- /MAT/LAW62
- Ogden (Hyperelastic materials)
- /MAT/LAW70
- Visco-elastic tabulated (solids)
- /MAT/LAW77
- Visco-elastic tabulated with porosity and air flow
Visco-elastic Plastic Law
- /MAT/LAW33
- Visco-elastic plastic (solids) and user-defined yield function
- /MAT/LAW52
- Gurson, visco-elasto-plastic porous metals, and strain rate dependent
- /MAT/LAW66
- Semi-analytical plastic model. Yield surface built from curves in tension, compression and shear + /VISC/PRONY
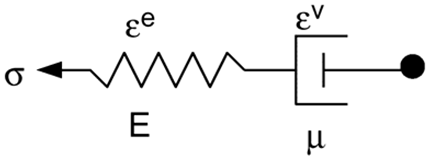
Figure 8. Maxwell Model
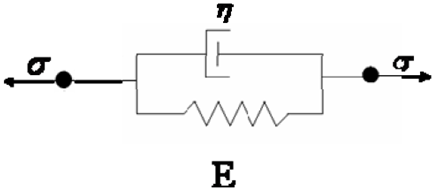
Figure 9. Kelvin_Voigt Model